In this introduction, we explore the critical responsibilities of a Registered Behavior Technician (RBT), including:
Lecture 2: Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Children’s growth and nourishment is not limited to their physical aspects only. From their birth till the age of five years, they are expected to meet various milestones. These milestones include:
- Social smile (or smiling while seeing their parents, siblings, etc.)
- Neck holding.
- Pincer grasp.
- Holding objects and playing with them.
- Speaking, etc.

If there is a delay in the manifestation of these milestones, then it might hint towards a developmental condition, such as autism.
What Exactly is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental condition that typically becomes evident by age three and continues throughout life. The presentation of symptoms can vary significantly, with some individuals experiencing mild signs, while others may show a broader range of characteristics. In recent years, the prevalence of ASD has increased in the USA.
The CDC data from 2014 shows that every 1 out of 68 children in the USA is diagnosed with ASD. The condition affects individuals across all ethnicities and races, however, boys are five times more likely to be diagnosed with ASD than girls.
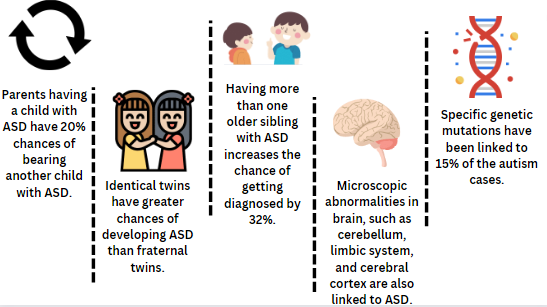
What is Causing a Climb in the Rates of ASD?
Advanced parental age: Researchers at Columbia University determined that the advanced parental age can increase the chance of having children with autism by 11%.
Changing diagnostics: With changes in diagnostic practices, clinicians can now identify children with ASD more easily than before.
Increased education and awareness: Parents and guardians are more aware of ASD, and they also educate others on this issue. The likelihood of children getting diagnosed with ASD has increased.
Lecture 3: Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) & its Causes
Diagnosing ASD
A timely and accurate diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential, as it helps in understanding the unique needs of the child and creating an appropriate support plan. A diagnosis can highlight the strengths and challenges of children with ASD, allowing them to grow and learn at their own pace in a way that best suits their individual needs.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is not diagnosed through medical tests. A diagnosis is made by a qualified healthcare professional, such as a doctor or psychologist, who has specialized knowledge in assessing children with communication and behavioral differences. They use a comprehensive evaluation process to understand the child’s unique strengths and challenges.
Common professionals involved in diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) include:
- A developmental pediatrician
- A child psychologist
- A pediatric neurologist or psychiatrist

Other professionals, such as speech-language pathologists and special educators, may be involved in supporting the child’s development after diagnosis, but they are not typically responsible for making the diagnosis.
Are there Known Causes of Autism?
The exact cause of autism is not yet fully understood. However, it is widely accepted that autism is related to neurological and biological factors, which can vary from person to person.
Roles of BCBAs vs. RBTs and how these professionals collaborate in behavioral intervention. This lecture sets the stage for the comprehensive learning experience ahead, equipping you with real-world insights and practical strategies to confidently approach ABA therapy and crisis management.
Lecture 4: Key Challenges in ASD

Impairment in Social Interaction
Difficulties with social interaction are a key characteristic of Autism Spectrum Disorder. These challenges may be seen in nonverbal behaviors, such as diminished facial expressions, not maintaining eye contact, and non-regulated social interaction. Children with ASD may also experience differences in recognizing social cues and expressing emotions.
Verbal and Non-verbal Communication
In children with ASD, challenges with verbal and non-verbal communication can show up in the following ways:
- Delayed development (or lack ) of spoken language. This is not accompanied by compensation of alternative communication modes, such as miming or gestures.
- Repetitive language or use of highly individualized language.
Individuals with ASD who have well-developed speech may still have difficulty starting or sustaining conversation with others.
What Behaviors and Activities may typify ASD?
Individuals with ASD are often engaged in stereotypical behavior(s) with intense focus such as:
- Adhering to specific and non-functional rituals.
- Repetitive behaviors, such as finger twisting or moving the whole body again and again.
- Preoccupation with several objects (or parts of objects).
Lecture 5: Recognizing the Indicators of Autism & Comorbid Conditions
Indicators of Autism
Following are some indications that a child may have autism.
| Social Differences | Communication Differences | Behavioral Differences |
| Not initiating an activity | Becomes apparently deaf | Throws tantrums often |
| Fails to respond to names | Impaired non-verbal communication | Becomes hyperactive or opposing to others |
| Not using hand gestures or facial expressions | Absent and diminished spoken language | Displays unusual reaction to sensory stimuli |
| Does not engage with peers | Cannot entirely express their desire | Not accepting change in routine environment |
Remember, ASD is a spectrum, meaning it affects individuals in a wide range of ways, and some children may not display the stereotypical behaviors commonly associated with the condition.
Comorbidities Associated with ASD
Various comorbidities are associated with ASD, such as
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
- Anxiety disorders.
- Adjustment disorders are associated with depression, anxiety, mood disorders, and conduct.
- Disruptive behavioral disorders.
- Mood disorders.
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD).
